The standard was published as VDA 19 and is still valid today in several updated versions. The international counterpart to VDA 19 is the ISO 16232 standard, the current 2018 version of which is fully compatible with VDA 19 Part 1.
Among other things, VDA 19 describes how components must be cleaned, tested and packaged in order to avoid contamination by particles or liquids. The regulations comprehensively define the requirements for the technical cleanliness of components in the automotive industry. Sectors outside the automotive industry, such as precision mechanics and the optical industry, also benefit from the suggestions on how to achieve clean production.
In order to achieve technical cleanliness, measures are taken to reduce the formation of particles in the process, among other things. The use of CNC cleanrooms is an important aspect of VDA 19, as they provide a controlled environment for cleaning and testing components. In a CNC cleanroom, particles on surfaces are measured to monitor cleanliness. In contrast to cleanroom production, the particle size to be avoided is usually in the visible range (> 50 µm). The measurements are carried out using washing tests and optical methods. The particle sizes in CNC cleanroom production may be up to 600 µm or even larger depending on the process. More important than the size is often the type of particle that can affect production, e.g. the presence of metal particles.
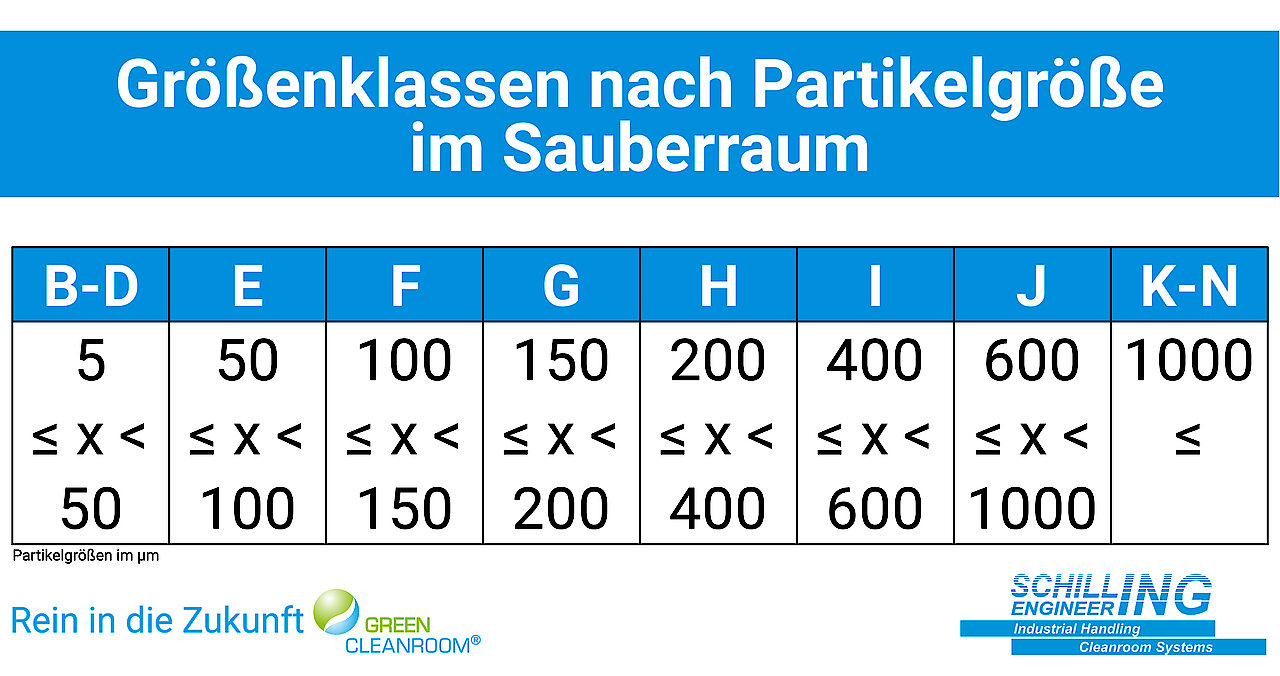
Cleanliness levels and number of particles in technical cleanliness according to VDA 19
The VDA defines four cleanliness levels for technical cleanliness in assembly. The higher the cleanliness level, the lower the number and size of particles present on the parts. The four levels are
SaS0: non-regulated area
In this area, no special measures are taken to prevent or minimize particle contamination. The ambient conditions correspond to those of a normal industrial hall.
SaS1: Clean zone
In this area, measures are taken to reduce the introduction of particles from outside and the carry-over of particles via the process chain. The production environment is access-restricted and controlled.
SaS2: CNC Cleanroom
In this area, in addition to the measures for a clean zone, further ventilation conditioning measures are taken to reduce the introduction of particles by means of filter systems.
SaS3: Cleanroom
In this area, the highest demands are placed on technical cleanliness. Access is via airlocks. The environmental conditions correspond to those of a clean room in accordance with EN ISO 14644.
It should be noted that VDA 19 does not prescribe any specific cleanliness, but refers to the individual requirements of the respective cleanliness specification. The choice of cleanliness level depends on the type and degree of contamination of the components.
In most cases, cleanliness level 2 adequately fulfills the requirements for clean assembly if hazardous particles need to be reduced.
CNC Cleanrooms in which the concentration of particles is monitored and regulated are therefore a key aspect of VDA 19, as they provide a controlled environment for cleaning and testing components. The permitted number of particles is measured and recorded in steps of 5 µm - 1000 µm on the surfaces using washing tests and optical methods (see table). The permitted number of particles is not defined by the VDA, but is determined for each process. More important than the size is often the type of particles that can affect production, e.g. the presence of metal particles.
The particle sizes significantly exceed the particle sizes permitted in a cleanroom.
CNC Cleanrooms are therefore generally easier to set up and cheaper to operate than a regulated cleanroom with complex filter and ventilation technology.